2 Department of Animal Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran.
3 Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Faculty of Agriculture, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran.
*Author for correspondence: Vahid Iranpur-mobarakeh, Department of Animal Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, P.O.Box 115, Iran, e-mail: iranpur2010@yahoo.com Fax number: +98 3814424412
Source: Vahid Iranpur-mobarakeh, Department of Animal Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran
Abstract: None of the procedures yielded DNA of suitable purity for SSR and other PCR assays for DNA that was stored at 4ºC on prolonged period. We established an improved procedure for rapid isolation of DNA from sheep’s blood and other species stored at 4ºC for up to one year or more and suitable for SSR analysis and other PCR-based applications
Date Added: 2010-05-02
Date Modified: 2010-05-02
Introduction
PCR-based methods are widely used in plants and animals for marker-assisted breeding and high-resolution mapping. These studies require analysis of large number of samples, thus a DNA extraction method, which is fast, inexpensive and yields high quality DNA, is desired. Several methods for extraction of genomic DNA from blood, tissue, sperm, tooth and bone have been examined and demonstrated so far. Also this subject has been developed by improvement of science [1, 2]. The quality of DNA extracted from liquid blood is not adversely affected by storage at 4ºC for up to 24 h [3]. Small but significant changes have been observed in metabonomic studies in samples of blood maintained at 48°C for 36 h [4]. DNA has been extracted from leucocytes and on prolonged storage of whole blood at -20 and -80ºC, DNA yield was considerably decreased which was probably due to degeneration of the white blood cells in the storage of long period. We have now modified the method for rapid isolation of DNA from blood. The DNA is suitable for SSR analysis and other PCR-based applications.
Materials and Methods
Blood collection
Blood should be collected in EDTA-containing vacutainer tubes. As will all body
fluids, blood represents a potential biohazard, thus care should be taken in all
steps requiring handling of blood. If the subject is from a known high-risk
category, additional precautions may be required. Blood samples can be stored at
room temperature for DNA extraction within the same working day or at
refrigerator for later uses.
Standard chemicals
This method uses standard chemicals that can be obtained from any major
supplier; we used chemicals supplied by Sigma Co. as follow:
- EDTA (0.5 M), pH 8.0: Add 186.1 gr of anhydrous EDTA to 800 ml of distilled water. Adjust pH to 8.0 with NaOH pellets. Make up to 1 liter with distilled water. Autoclave at 15 p.s.i. for 15 min.
- 1 M Tris-HC1, pH 7.6: Dissolve 121.1 gr of Tris base in 800 ml of distilled water. Adjust pH with concentrated HCl. Allow mixture to cool to room temperature before finally correcting pH. Make up to 1 liter with distilled water. Autoclave at 15 p.s.i. for 15 min.
- Preparation of Red blood cell lysis buffer: 0.01 M Tris-HCl pH 7.6, 320 mM sucrose, 5 mM MgC12, 1% Triton X 100. Add 10 ml of 1 M Tris, 109.54 gr of sucrose, 1.01 gr MgC12, adjust pH to 8.0 and finally add 10 ml of Triton X-100 to 800 ml of distilled water, and make up to 1 liter with distilled water. Autoclave at 15 p.s.i. for 10 min. Sugars at high temperature can cause caramelization (browning), which degrades the sugars [5].
- Preparation of Nucleic lysis buffer: 0.01 M Tris-HC1, 11.4 mM sodium citrate, 1 mM EDTA, 1 % sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS). Take 10 ml of 1 M Tris-HC1 (pH 7.6), 3.75 gr of anhydrous EDTA (pH 8.0), 10 gr SDS, 2.94 gr of sodium citrate, and adjust pH to 8.0. Make up to 1 liter with distilled water. Autoclave 15 min at 15 p.s.i.
- TE Buffer, pH 8.0: Take 5 ml of 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 2 mL of 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8, and make up to 1 liter with distilled water. Adjust pH to 8.0 and autoclave 15 min at 15. p.s.i.
- Chloroform prechilled to 4°C.
- Ethanol (100%) prechilled to -20°C.
Procedure of DNA Extraction
Before starting DNA extraction, liquid blood venogects should be shake gently by
rotating blood mixer (vortex)
- Pour 500 µl of blood into a 1.5 ml eppendorf tube and add 1000 µl of red cell lysis buffer.
- Shake microfuge tube gently (up to homogenizing), then spin for 2 minutes at 7000 rpm.
- Discard supernatant and repeat steps 1-3 two or three more times to remove hemoglobin. It is important to breakdown the pellet by vortexing and rinses it well in red blood cell lysis buffer in order to clean the white blood cells from residual of hemoglobin.
- Placing the tube on tissue paper for few seconds downward. Be careful from cross-contamination between different samples.
- Add 400 µl of nucleic lysis buffer to eppendorf tube. Note: if the pellet formed, you must pipette the pellet up to dissolve it.
- Add 100 µl of saturated NaCl (5M) and 600 µl of chloroform to eppendorf tube and mix on a rotating blood mixer at room temperature then spin it for 2 minutes at 7000 rpm.
- Transfer 400 µl of supernatant to a new 1.5 ml tube.
- Add 800 µl of cold (-20°C) absolute Ethanol and shake it gently then vortex it. DNA should appear as a mucus-like strand in the solution phase.
- Spin the microfuge tube for one minute at 12000 rpm to precipitate, then discard supernatant carefully and let tube be completely dried in room temperature (Place Eppendorf tube downward on the tissue paper).
- Add 50µl of TE to it then vortex; keep eppendorf tube of DNA in 4°C or -20°C for later uses. We routinely use about one µl per PCR reaction without adverse affects. DNA can be quantified and diluted to a working concentration at this point or simply use 1 µl per PCR reaction. We expect that the yield of this procedure be 100 to 300 ng/µl, DNA. Using the above method, high quality DNA samples from a sheep population were extracted for gene mapping studies.
Results
The quality and quantity of extracted genomic DNA were controlled. High quality DNA was obtained using our method. All of the samples including blood samples stored at 4ºC for one year and other samples stored in different conditions were able to profiling for SSR and other PCR applications. Agarose gel 0.8% was used for quality control of genomic DNA. Extracted genomic DNA by our method on Agarose gel 0.8% , SSR amplification on polyacrylamide gel 6% and Digestion of DNA with EcoR1 restriction enzyme are given in Figure 1. The yields of the DNA samples ranged from 1.0 to 3.0 µg from 500µl blood that was stored at 4ºC for one year. This amount of DNA is enough to conduct 200 to 300 PCR reactions.
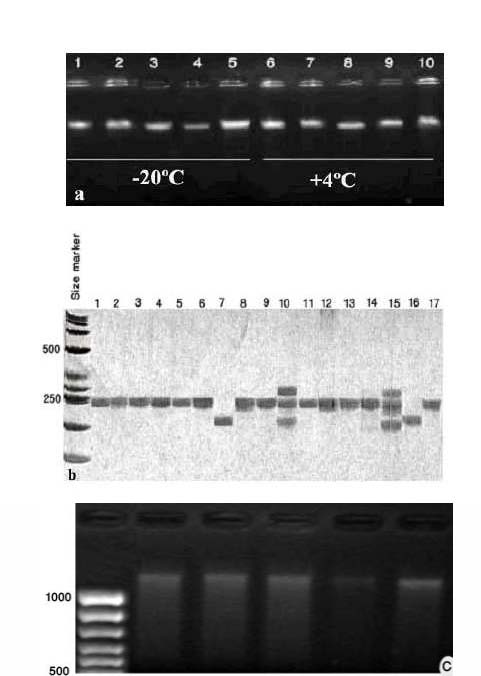
Figure 1. a) Genomic DNA extracted from whole blood of the sheep using the rapid isolation method on agarose gel; Lanes 1 to 5 and 6 to 10: DNA extracted from whole blood stored at -20ºC and +4ºC for one year, respectively. b) Microsatellite PCR analysis of DNA samples isolated by the rapid isolation method on polyacrylamide gel. The DNA samples were amplified for MCM137 marker from whole blood that was stored at +4ºC for one year. c) Digestion of DNA samples with EcoR1 restriction enzyme.
Discussion
Extracted genomic DNA from different biological samples is used widely in medical genetic laboratories for diagnosis of genetic disease and in forensic and research centers and laboratories. In our method, genomic DNA can be extracted in the least time and with high quality and quantity by using simple materials and equipments.
Not only was high quality DNA extracted from blood that was stored at 4ºC, this
method also worked well for extracting DNA from the other blood samples that
were stored at -20ºC or -80ºC. In a workday, one person can complete DNA
isolation from more than 50 blood samples using this method. This method has
been routinely used to extract DNA from whole blood of sheep for PCR based
applications in our laboratory but it can be used for other species such as
human. This method has several advantages such as; economical spending, no need
to the specialized and expensive equipments, spending little time, no need to
the experimented and experienced staff and more important, DNA extraction from
whole blood stored at usual fridges for long time. In this method, genomic DNA
with high quality and quantity can be acquired from different biological sources
such as blood, bone etc. Time of extraction of genomic DNA in our method is less
than one hour.
Acknowledgments
The authors offer grateful thanks to Shahrekord University for financial assistance; as well as to the staff of Shuli Animal Breeding Center (SABRC, Shahrekord, Iran) for providing blood of sheep.
References
- Bailes,S.M., Devers,J.J., Kirby,J.D. and Rhoads,D.D. (2007) an inexpensive, simple protocol for DNA isolation from blood for high-throughput genotyping by polymerase chain reaction or restriction endonuclease digestion. J. Poultry Science 86:102–106.
- Ali,S.M., Mahnaz,S. and Mahmood,T. (2007) Rapid genomic DNA extraction (RGDE). Protocol Online PID: 4791, http://www.protocol-online.org.
- Antony,H., Paul,R., Yancy,R., Nicola,T., Alice,D., Rupert,G. and Stephen,L. (2007) The quality of DNA extracted from liquid or dried blood is not adversely affected by storage at 4ºC for up to 24 h. International Journal of Epidemiology 2008;37:i7–i10.
- Tim,C.P. and Paul,E. (2007) The UK Biobank sample handling and storage validation studies. International Journal of Epidemiology 2008;37:i2–i6. 5.Bartlett,J. and White,A. (2003) Extraction of DNA from Whole Blood. Methods in Molecular Biology, 10.1385/1-59259-384-4:29.
http://www.protocol-online.org
© 1999-2009 Protocol Online, All rights reserved.
